Cloud Computing in the Oil & Gas Industry: Use Cases

Today, technology like cloud computing in oil & gas industry is becoming very important. As the energy sector moves towards digital transformation, companies are now seeking to shift from traditional IT systems. Solutions developed with cloud computing technology provide a secure and quicker way to handle a large volume of data.
The oil and gas industry has always faced many complex problems, starting from fluctuating oil prices, safety risks, and operational costs to difficulty in extracting insights from data. Cloud computing in the oil and gas industry solves all these problems that traditional, slow, and expensive IT systems couldn't.
A recent report depicts that the global cloud computing in oil & gas market was valued at USD 2.7 billion in 2024 and is predicted to register a CAGR of 7.3% between 2026 and 2034. This shows how companies are leaning towards cloud computing to move their applications to a single cloud that would help in workflows and team collaborations. Also, this infrastructure will help in remote monitoring and control capabilities, decreasing operational costs.
So, do you also want to integrate cloud computing oil and gas? If yes, then this guide explores everything from start to end in the context of the cloud transformation oil and gas sector, which includes how cloud computing is changing this industry, what technologies are used in it, real use cases, and what the future trends are.
Why Oil and Gas Industry is Turning to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is not a one-sided solution but a form of technology that can be used in numerous applications throughout the oil and gas sector. Companies are adopting various concepts of cloud models and cloud services to enhance their operations and data management, as well as reduce costs. These are fundamental technologies that require an understanding in any attempt to plan a digital transformation in this industry.
Different Types of Clouds
The oil and gas industry often operates across different geographies, sites, and regulatory environments. Here are three different cloud types oil and gas industry that are widely used:
Public Cloud
Third-party vendors offer this service, like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), or Google Cloud. They provide elastic infrastructure and are otherwise used on non-sensitive workloads such as collaboration platforms or dashboard analytics in real-time.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is constructed and specifically designed to serve a single organisation. It has greater control in terms of data and infrastructure. It is often utilised to deal with highly sensitive data, e.g., reservoir simulations or proprietary seismic models.
Hybrid Cloud
This is a mix of cloud and the private cloud. Hybrid environments enable corporations to securely process critical business functions in a private cloud and rely on the public cloud for scalable storage and analytics. The concept of a hybrid model has become the most preferred approach among today's oil and gas companies due to the flexibility, compliance, and cost management it provides.
| Aspect | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| Cost | Low upfront cost; pay-as-you-go model | High upfront cost; ongoing maintenance required | Moderate; balances cost and control |
| Scalability | Highly scalable and flexible | Limited by in-house resources | Scalable; can offload workloads to public cloud when needed |
| Security | Secure but shared environment | High security, controlled internally | High security with flexibility; sensitive data stays private |
| Compliance | May not meet all oil & gas-specific regulatory requirements | Easier to customise for compliance needs | Can segment data/workloads to meet compliance |
| Performance | May vary depending on provider and internet connectivity | Consistent performance optimised for enterprise needs | Combines reliability of private with flexibility of public |
| Use Case in Oil & Gas | Real-time data analytics, collaboration, and mobility | Seismic data storage, regulatory-sensitive workloads | Seismic data storage, regulatory-sensitive workloads |
| Examples | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud | On-premise VMware, OpenStack | Microsoft Azure Stack, AWS Outposts, IBM Cloud Satellite |
SaaS, PaaS, IaaS in the Cloud Industry
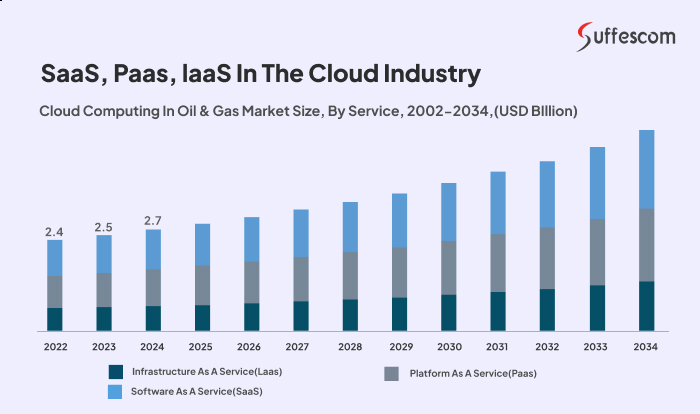
Cloud services are delivered in different models, depending on the need:
- Software as a Service (SaaS) is widely used for applications like HSE compliance tools, supply chain management platforms, and reporting systems.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) is the best option for creating custom software in the oil field, like asset-tracking dashboards or mobile inspection applications, with no management of servers.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides the capability of on-demand virtualised computing resources when a large-scale computing task is to process seismic datasets or perform simulation modelling.
Edge Computing
Edge computing oil and gas can pre-process data locally, at some proximity to each other or to each of the drilling locations, production activities, or pipelines, only to forward pertinent data to the cloud. This minimises the cost of latency and bandwidth. With cloud, edge computing allows real-time decisions to be made about remote or offshore activities.
Cloud-Native Applications
Contemporary oil and gas software development involves the utilisation of cloud-native technology and microservices more and more frequently. This implies that applications will be built to work in the cloud. Microservices architecture enables modification or expansion of specific components of an application, such as the drilling analytics module, without requiring changes to the entire application. It makes the process more agile and less downtime.
How Cloud Computing Is Changing All the Sectors of the Oil & Gas Industry
In the last 10 years, the oil and gas industry has embraced many technologies, but the problem comes in integrating them. This creates problems in their work. And the complexity has grown since then. In this scenario, cloud computing is becoming a transformative solution for businesses to simplify their operations. Here’s how this technology is changing all three segments of the oil and gas industry:
Upstream
Discovering new reservoirs can be costly, and there is no certainty, which leads to millions of investments with no guaranteed success. This risk prompts the upstream sector to adopt more innovative technologies that can achieve a higher level of accuracy and reduce financial exposure. After having all the data from seismic readings, core samples, and drilling records, turning it into insights is still an issue that requires computational power.
This is where cloud application development services are revolutionising upstream operations. With scalable computing, complex geological simulations that once took weeks can now be done in just days. These cloud-powered systems can also find patterns across geological formations, supporting more informed decisions. Moreover, cloud platforms boost the creation of detailed 3D subsurface models, allowing geologists to interpret underground structures with the best precision and speed. The key activities of this segment are:
- Geological Surveys
- Seismic studies
- Drilling and Well Completion
Midstream
The midstream sector helps in transporting oil and gas from production sites to refineries and end users. As production of energy increases, so does the requirement for extensive infrastructure. Many pipelines of thousands of miles are being constructed to meet this requirement, but this expansion also raises concerns about safety, reliability, and environmental risks.
Again, cloud computing is coming out as a powerful tool to aid operators in managing these problems. With cloud-integrated systems, businesses can run predictive maintenance that finds out the initial signs of errors or failures.
Midstream operations encompass collaboration with stakeholders. Cloud-based tools streamline communication, allowing all parties to access accurate, up-to-date information when needed. And, it also helps operators to receive alerts if there are any leaks or mechanical issues. Key operational priorities in this segment include:
- Pipeline transportation and integrity monitoring
- Storage and transfer facilities
- Stakeholder coordination and compliance reporting
Downstream
This segment of the oil and gas industry is where raw crude oil is refined into valuable end-products, such as gasoline, diesel, and many more. Due to this, these operations involve intricate processes that need very high precision, efficiency, and optimisation. Small improvements can lead to cost savings and increased margins in this segment.
Cloud computing technology is playing a critical role in transforming downstream operations. Refiners generate large volumes of data, and cloud computing enables this data to be processed, providing better workflow suggestions and optimising operations.
Another significant benefit is that it provides the ability to gain deeper market intelligence. Analytics tools powered by cloud computing help depict insights into customer demand, price fluctuations, and inform better decisions. Core focus areas in the downstream segment include:
- Refining and processing
- Storage and inventory management
- Distribution and marketing of petroleum products
Why Oil and Gas Industry is Turning to Cloud Computing
The oil and gas industry is under increasing pressure to be more efficient, make decisions more quickly, and work with vast amounts of complex data. The demands have put traditional IT systems in a tight spot. Cloud computing offers a viable solution, as companies in this sector will become more agile, reduce their operational costs, and better respond to rapid changes. Let's take a look at some benefits of how the oil and gas industry is turning to cloud computing:
Increasing Data Capacity and Exploration
The sources of data generated by exploration and production activities include seismic surveys, drilling sensors, and geological models, which can amount to a substantial amount. On-premise systems are costly and slow when it comes to managing this data. That’s where cloud-based platforms enable more businesses to store and process large-scale amounts of data more efficiently. This will not only decrease the delay in decision-making but also facilitate better predictions of resources and analysis of reservoirs.
Demand for Agility & Faster Decision Making
The oil and gas environment is one of high risk, where swift decision-making is crucial. The firms require agile application development and the immediate availability of data for modifying drilling plans or decisions in response to fluctuations in market conditions. Cloud computing is facilitating this by allowing access to dashboards, operational data, and predictive analytics in real-time with other teams across the globe.
Cost Pressure and Need For Operational Efficiency
Oil prices are high, and the profit margin is often narrow. Maintaining the physical IT infrastructure across various locations is expensive and rigid. Cloud computing reduces capital costs by shifting the payment system to a pay-as-you-go model. This enables firms to manage expenses while maintaining access to available resources whenever needed.
Remote and Automated Operations Becoming Critical
Most oil and gas properties are situated offshore or in remote locations. Observation and operation of such places are highly costly and hazardous to do manually. The remote operations supported on the cloud platform are facilitated through the integration of IoT sensors, automation, and control centres.
This enables equipment to be tracked, faults to be identified before they become problems, and incidents to be responded to with a greater level of speed, enhancing not only safety but also performance.
Ready to integrate cloud-based solutions in the Oil and gas sector?
Connect with our app development company to simplify your operations.
In-Depth Benefits of Cloud Computing for the Oil and Gas Sector
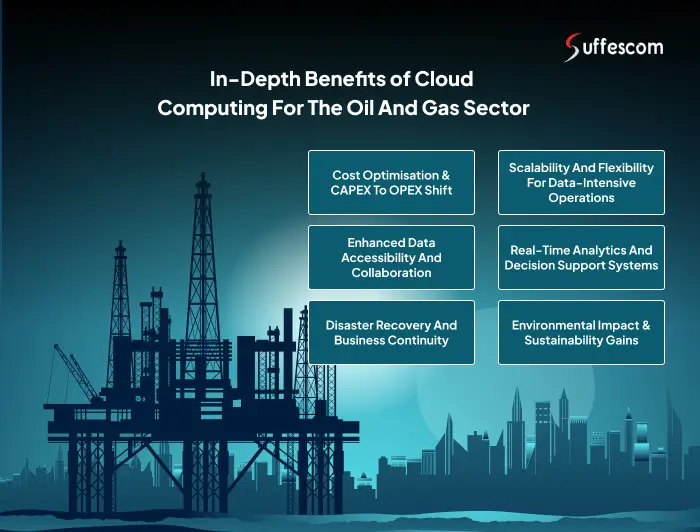
After knowing how cloud computing is helping the oil and gas industry, we have checked out how it has changed the whole infrastructure and system. Now, let’s explore its in-depth benefits for the oil & gas industry:
1. Cost Optimisation & CAPEX to OPEX Shift
- Lowers infrastructure expenses: There are expenditure costs of framework servers and data centres, which means cloud computing eliminates the costs related to substantial infrastructure.
- Pay-as-you-go pattern: Organisations are charged only for the payments made upon consumption of the resources they utilise, whether it be storage, computer power, or analytics tools. This also provides an advantage in budget maintenance, particularly during periods of price changes.
- Reduced costs of maintenance and upgrades: Cloud vendors' control of system updates, security patching, and hardware upgrades. This saves on the internal IT teams and makes work more efficient.
- Case in point: With hybrid cloud infrastructures, businesses have seen considerable amounts of savings in terms of time and money.
2. Scalability and Flexibility for Data-Intensive Operations
- Perfect for peak operations: Cloud platforms must be able to support more workloads without downtime or service interruption, whether the task is performed during an exploration operation or an emergency.
- No capacity constraints: Cloud services have the ability to scale worldwide and in real-time, whereas physical systems have capacity constraints, which means they lack elasticity, a critical requirement in current oil and gas processes.
- Scales with heavy data volumes: The cloud infrastructure can scale with ease to handle voluminous datasets involved in seismic imaging, drilling sensors, and production monitoring.
- No capacity constraints: Cloud services can scale worldwide and in real time, where physical systems have capacity constraints, hence lack elasticity, which is critical in current oil and gas processes.
3. Enhanced Data Accessibility and Collaboration
- Centralised cloud data leaks: With cloud computing in the oil and gas industry, there are very few chances of cloud data leaks due to its security-driven approach, which provides a safe way to manage workflows.
- Enhanced decision-making: With cross-functional teams able to work on reports, share project updates, and review live dashboards in real-time, there is no version conflict or delay in making a decision.
- Accessibility without compromising data security: Data is secure, as it is possible to customise access according to the role and to business units to facilitate efficient collaboration.
4. Real-Time Analytics and Decision Support Systems
- Live dashboards and alerts: The cloud-based solutions provide real-time visualisation to determine drilling performance, machinery status, and safety indicators.
- Integration of AI and machine learning: The cloud can host predictive models to prevent equipment failure and even recommend the course of action.
- Let one become more operationally agile: The decision-makers can limit downtimes and eliminate the costly waiting with fast decision-making.
- Enhanced planning and risk mitigation: The accuracy of forecasting in the fields of exploration, production, and logistics can be enhanced with the help of accurate data.
5. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
- Automated data backup: Regular backup facilities for data are available automatically in cloud services, offering protection of mission-critical data without any manual action.
- Systems that are geographically distributed: Information is stored in numerous regions, and there is a guarantee of availability in case one region is affected.
- Reduces downtime: Downtime is minimised as in the event of a natural disaster or failure in the system, the business can be back up and running from replication sites.
- Lowers recovery cost: Cloud-based recovery is fast, reliable, and inexpensive, relative to the older disaster recovery systems.
6. Environmental Impact & Sustainability Gains
- Green infrastructure: Major cloud companies operate efficient data centres by using green technologies, which consume low energy and make use of renewable energy sources.
- Physical footprint reduction: Businesses that are using cloud computing will no longer need a high number of physical servers and data rooms in their offices, thus shrinking their carbon footprints.
- Enables remote working: The capacity to access the cloud allows teams to work anywhere, which minimises the carbon footprint of travelling and office rentals.
- Signs with ESG Goals: Cloud computing can align with the wider environmental, social, and governance agenda relating to a reduction in waste and increased resource efficiency.
After discovering its in-depth benefits, let’s explore its uses in the oil and gas industry.
Real-World Use Cases of Cloud Computing in Oil and Gas
The use cases of cloud computing are not limited to data storage or cost savings. Let’s discover some of them:
1. Exploration & Seismic Data Processing
- Enables high performance computing (HPC): Cloud lets you crunch large seismic datasets and elaborate geological models in less time compared to the large IT systems.
- Enhances data accuracy and accessibility: Data from various differentiated sources can be uploaded, accessed, and interpreted in a single cloud-based environment by the exploration teams.
- Reduces cycle times: Where weeks of processing were once required, it can now be achieved in days, accelerating drilling approvals and project start-ups.
- Facilitates cooperation: When people are working on a scale, they can collaborate on models without having to manually send data files that are large.
2. Predictive Maintenance Powered by Cloud AI
- Enables condition-based maintenance: AI models in the cloud examine operational data from equipment to predict possible failures.
- Minimises equipment downtime: The equipment is only maintained when there is a need, and this prevents cases of over-maintenance as well as cases of sudden collapse.
- Increases asset reliability: Constant monitoring of assets increases the life of important equipment like pumps, compressors, and valves.
- Improves the safety of the worker: A major safety benefit is the ability to detect faults early enough, thus avoiding issues that lead to accidents due to faults with the equipment.
3. Supply Chain & Inventory Management
- Automates the tracking of materials: A cloud-based software allows tracking of the end-to-end inventory positions in the warehouse, rigs, and remote locations.
- Enhances delivery schedules: The coordination of shipments to minimise delays is possible with the help of integrated cloud tools.
- Reduces operational cost: Businesses do not have to spend more money to make an emergency order because of the real-time data on the inventory.
- Facilitates vendor management: Contract, invoice, and purchase record management is handled at junior levels through cloud storage.
4. Health, Safety & Environment (ESG) Compliance
- Makes safety reporting a standard: The field workers can further report on occurrences and inspections via mobile apps linked to the cloud, where the information is recorded in real-time.
- Respond to incidents quicker: In the event that a safety issue is reported, notifications across departments are automated, which increases investigation and containment speed.
- Enhances regulatory compliance: Cloud systems will have the latest records to be audited and will comply with local, regional, and international safety regulations.
- Centralised Training and documentation: Manuals, training videos, and updates in policies are all deposited in a safe cloud environment that can be reached from remote locations.
Challenges and Risks of Cloud Adoption in Oil and Gas

There are a lot of challenges that businesses face while incorporating cloud computing in their processes and infrastructure, but overcoming these challenges will give an infrastructure and quicken everything.
1. Data Migration & Complexity
- Integration of legacy systems: Some oil and gas firms still operate on old systems and applications, which reside in their offices or data centres. To migrate this data to the cloud, custom integration is needed, which takes time and money.
- Migration downtime: Moving critical applications can mean taking certain applications offline. This may have operational inefficiency when there is a lack of planning for the same.
- Data validation, consistency: In consistent data validation or even consistency, all the data that is being migrated to the cloud environment must also remain usable and thus should be thoroughly validated.
- Compliance and data governance: Firms must establish the appropriate data governance during the migration process, particularly when handling sensitive data in regions where data residency is strongly protected.
2. Skills Gap & Workforce Transformation
- Insufficient talent pool: The oil and gas industry can be short of the internal talent trained in the cloud platforms, cybersecurity, and DevOps.
- Requirements of perpetual education: Even after the preparedness of the skilled team, they must be trained in cloud-native instruments and services, which undergo rapid changes.
- Resistance to change: Staff members might fear using new ways of doing things without much knowledge of them, hindering digital change.
3. Vendor Lock-in & Multi-Cloud Strategies
- Dependency on a single provider: There is a tendency to defer entirely to a service provider and end up with rigid contracts, low innovation, or switching costs.
- Lack of interoperability: A transfer of the workload proved to be cumbersome when applications were constructed using proprietary methods.
- Multi-cloud as a solution: Being able to utilise different cloud providers better enables costs to be controlled, risks to be managed, and various regulations to be adhered to across regions.
- Platform governance: The issue of granting access and overseeing the performance of multiple clouds, as well as the level of their security settings, may be complicated without organising tools and policies.
What Are the Best Practices For Cloud Migration?
There are several practices for cloud migration in the oil and gas industry all over the world. Let’s explore some of them, which you can implement smoothly and that help you gain better insights.
1. Stepwise migration approach
- Start small but grow steadily: Initiate with small and non-vital systems or a small pilot run to trial performance and overcome initial difficulties.
- Set measurable objectives: Have clear objectives that you want to attain with cloud migration, including cost reduction, access to data, or operational responsiveness.
- Rank prioritisation of workloads: Not all the applications should be relocated immediately. Target, in the first place, those that can gain the most out of the cloud capabilities, i.e., analytics, collaboration tools, or backup systems.
2. Assessment and planning phase
- Assess your existing infrastructure: undertake a thorough examination of what is currently in use, including dependencies, gaps, and cloud-ready workloads.
- Engage business units in early consideration: Encompass the operations, engineering, and HSE departments to synchronise the IT strategic approach with the operations.
- Select the appropriate cloud model: The choice of a public, private, or hybrid cloud environment must be determined by compliance, cost, and flexibility.
3. Hybrid Cloud Adoption as a Transition Strategy
- Control Over Sensitive Systems: Keep the highly sensitive or regulated data on a non-public cloud and other workloads that are easily scalable to be on the public cloud.
- Balance security and performance: A hybrid setup can also give organisations an opportunity to explore the possibility of the cloud without relying entirely on third-party vendors.
- Continuous post-migration: Track performance and expenditure: With cloud-native tools, it is easy to track costs, system uptime, and resource utilisation.
- Update permissions and policies: Review and update access controls, backup policies, and security configurations on a regular basis to adjust in tandem with operational needs.
Future Trends: The Role of AI, Machine Learning, and Edge Computing in Cloud-Powered Oil and Gas
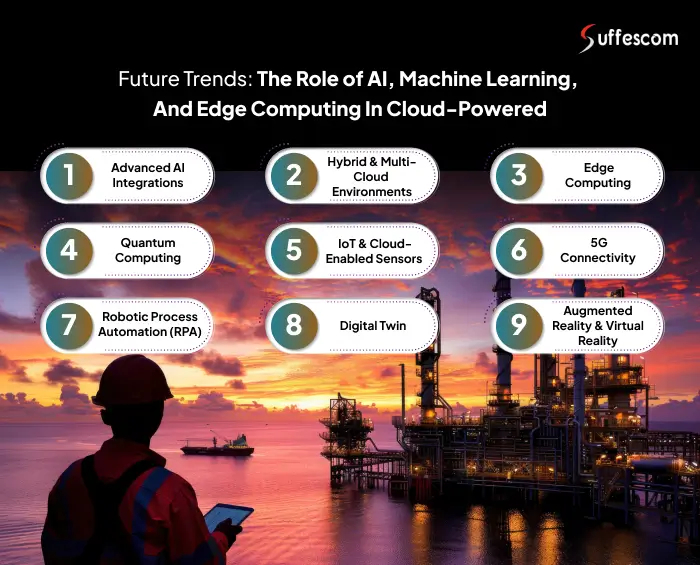
The influence of cloud technology is significant in the oil and gas industry, driving improved efficiency and growth in the sector. There are numerous future trends emerging in this domain, driven by cloud computing technology. Let’s explore some of the future trends that will shape this industry.
1. Advanced AI Integrations
In the near future, AI integration is going to help in more precise data analysis and predictive analytics, which helps in increasing the overall efficiency in equipment maintenance and operations.
2. Hybrid & Multi-Cloud Environments
These cloud environments provide the best flexibility in resource management and disaster recovery options. This approach will aid organisations in utilising both public and private clouds as they get control over sensitive information while optimising processes.
3. Edge Computing
This technology allows decentralised data processing, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by managing data near the source. Moreover, it allows more efficient data collection and analysis directly at the edge network.
4. Quantum Computing
To address complex situations and optimisation issues, quantum technology is used. This technology will help in exploration and drilling processes by solving problems that are currently not within the reach of classical computing.
5. IoT & Cloud-Enabled Sensors
Cloud computing integrated with IoT is bringing more power to the oil and gas industry. Cloud sensors are deployed at rigs, refineries and drilling sites so that enterprises are able to constantly monitor everything.
6. 5G Connectivity
5 connectivity with cloud sensors will provide more reliable and faster data transfer that will help in handling operations smoothly. This will help in operational visibility and enhance decision-making in difficult situations.
7. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Cloud Computing integrated with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can take the oil and gas industry to the next level by automating tasks and freeing up resources. This will help in taking strategic initiatives.
8. Digital Twin
In the oil and gas industry, digital twins that are cloud-based are now quickly gaining traction due to the health and monitoring of the performance of physical assets. By stimulating their behaviour, it helps to optimise schedules and prevent failures.
9. Augmented Reality & Virtual Reality
AR/VR with cloud computing can have a huge impact on the oil and gas industry. With AR/VR, workers can experience simulations of hazardous situations or situations that might occur in the future.
Real-World Examples of Cloud Computing in the Oil and Gas Industry
The highest ranking oil and gas firms are now seeking to use cloud to modernise, cut expenses and increase efficiency and here are some of the ways that the major players are leveraging cloud to remain competitive:
Shell: Smarter Operations with Microsoft Azure
Shell is leveraging Microsoft Azure to examine data across its global operations.. This will allow the company to track everything in real-time and will enhance quicker decisions to be made in the upstream and downstream operations, and will go in line with the broader objectives of digitalizing Shell.
ExxonMobil: Faster Seismic Data Processing
ExxonMobil uses cloud infrastructure to manage huge amounts of seismic information. The cloud increases data processing speed to gain faster and more accurate explorations and drilling, eventually lessening the prices and speed-to-market.
BP (British Petroleum): Improved Asset Management
BP maintains and monitors physical departments utilising cloud computing in the company. Bit by bit, with an improved maintenance plan and less downtime, BP maximises the assets' performance and maintains control of the cost of the operations.
Chevron: Streamlined Supply Chain
Chevron deploys the cloud to optimise logistics and inventory management. This enhances the movements of materials, reduces any delay and allows efficient scaling of operations to real-time-based demand.
TotalEnergies: Cloud for Sustainability
TotalEnergies applies cloud-based analytics to maximise energy generation, with environmental effects being monitored. This assists the firm in aligning the practices of operations to sustainability and regulatory compliance.
Equinor: AI-Powered Cloud for Safer Operations
Norwegian energy company Equinor uses cloud computing combined with AI to perform surveillance on offshore workplaces. This increases safety and gives us a better view of operations, and lowers the chances of equipment failure.
Petrobras: Cloud for Digital Twin Technology
Petrobras has also incorporated the use of cloud-based digital twins to replicate and track complicated offshore platforms in real time. The strategy will aid in offsetting spending on maintenance, enhancing safety and even optimising the field performance.
Traditional IT vs Cloud Computing in Oil and Gas
The change from traditional IT systems to cloud computing is an impactful technology transformation in the oil and gas sector. The table below highlights the key distinctions.
| Feature | Traditional IT | Cloud Computing |
| Cost Model | High upfront, maintenance costs | Subscription/pay-as-you-go |
| Scalability | Limited, hardware-constrained | Virtually unlimited, elastic |
| Data Accessibility | On-premises only | Accessible globally via the internet |
| Disaster Recovery | Complex, manual | Automated, geo-redundant |
| Innovation & Agility | Slow, long deployment cycles | Fast, continuous deployment |
| Security | On-premises control, but limited updates | Shared responsibility, rapid patching |
| Collaboration | Local network-based | Cloud-enabled global collaboration |
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud computing is not an option that the oil and gas industry should opt for; it's a necessity due to the advantages it provides. From decision-making to process, it helps in everything and helps businesses move forward in this domain with high accuracy. In this blog, we have seen each and everything that cloud computing supports in the oil and gas industry, what benefits it provides, and what the challenges are.
However, implementing it the right way is a crucial aspect that you need to keep in mind. Partnering with a mobile app development company will help you incorporate cloud-based solutions smoothly into your business operations.
If you are still unsure about where to start and how, then contact Suffescom today to boost your business efficiency in the oil and gas industry.
Step Into the Future of Energy with Cloud Innovation!
Automate, analyse, and scale your business with cutting-edge cloud solutions designed for oil and gas enterprises.
FAQs
How do cloud computing solutions help reduce operational costs in oil and gas?
Cloud Computing Solutions help reduce operational costs in the oil and gas industry by:
- Eliminating on-premise infrastructure
- Reducing maintenance costs
- Simplifies workflows and operations
What are the main cloud computing models used in oil and gas?
The main cloud computing models used in the oil and gas industry are:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
Will cloud computing help in cost reduction in the oil and gas sector?
Cloud computing helps in cost reduction in the oil and gas sector by cutting hardware, IT and maintenance costs.
What are the biggest challenges when migrating oil and gas IT systems to the cloud?
The biggest challenges when migrating oil and gas IT systems to the cloud are:
- Data Security & Compliance
- Managing large datasets
- Integration with legacy systems
- Need for skills and training
What role does AI play when combined with cloud computing in the oil and gas sector?
AI plays a crucial role when combined with cloud computing in the oil and gas sector by improving efficiency, security, supply chains, and mental sustainability.
What are the best practices for a successful cloud migration in oil and gas?
The best practices for a successful cloud migration in oil and gas are:
- Choose the right cloud vendor
- Evaluate migration
- Cost Efficiency
- Security & Compliance
Does cloud computing contribute to operational efficiency in the oil and gas sector?
Yes, cloud computing contributes to operational efficiency in the oil and gas sector by monitoring pipeline integrity and tracking environmental conditions.
What impact does cloud computing have on sustainability in the oil and gas industry?
Cloud computing has a significant impact on sustainability in the oil and gas sector by increasing operational efficiency, reducing carbon footprint, and much more.
How do oil and gas companies handle compliance and regulations in cloud environments?
Oil and gas companies handle compliance and regulations in cloud environments by:
- Incorporating robust security
- Applying automation
- Following industry standards
What future innovations are expected from cloud computing in the oil and gas sector?
The future innovations that are expected from cloud computing in the oil and gas sector are:
- AI-powered analytics
- Robotic Process Automation
- Cloud-based digital twins
- AR/VR Integrations
- Edge computing integration