Build vs Buy Software: The Complete Guide

The Build vs Buy Software decision has never been more critical as AI reshapes our technological landscape, with Statista forecasting the global AI market will exceed $1 trillion by 2031. With 2023 dubbed by McKinsey as "Generative AI's breakout year", businesses of all sizes face tough choices about their technology investments.
When weighing your options, cost considerations certainly stand out. Building custom software can range from $50,000 to millions, depending on complexity, while buying existing solutions typically involves lower upfront costs. However, the right decision requires going beyond just finances. A complete analysis must consider time to market, scalability, customization, and long-term maintenance.
In this guide, we'll walk you through a comprehensive framework to determine which path makes sense for your unique business needs. We'll explore how building custom solutions through a software development team can create a competitive advantage, and why purchasing ready-made options with AI integration or API integration capabilities is the smarter choice. Furthermore, we'll examine how this decision differs for startups versus enterprises, ensuring you have all the tools to make an informed choice that aligns with your business goals.
Software Build vs Buy: What is Best For Business?
The build vs buy software decision represents a crucial crossroad that profoundly affects your organization's trajectory. Making the right choice isn't merely about immediate costs—it's about aligning technology decisions with your business strategy and future growth.
Custom software delivers a unique competitive advantage by addressing specific business needs, essentially becoming a differentiator in your market. According to a McKinsey report, companies focusing on strategic technology investments achieve 20% higher revenue growth than their peers. Notable success stories include Netflix, whose proprietary recommendation engine now drives 80% of its viewership.
In contrast, purchasing off-the-shelf solutions offers immediate implementation benefits, reducing the time-to-market considerably. This approach typically involves lower upfront investment but may require compromises in functionality. The total cost of ownership (TCO) must be carefully analyzed, including both initial costs and ongoing expenses like subscription fees and maintenance.
Explore Custom Solutions with Suffescom
From AI integration to API-first development, Suffescom builds scalable solutions tailored to your business. Discover how our experts can help you innovate with confidence.
5 Key Factors Should Guide Your Build vs Buy Decision:
- Strategic Importance: Is this software a core differentiator for your business? Custom development makes sense for strategically important areas.
- Uniqueness of requirements: The more specialized your needs, the stronger the case for custom development through a software development team.
- Time-to-market: Need a solution quickly? Pre-built options with API integration capabilities are typically faster to deploy.
- Budget constraints: Custom solutions involve higher initial investment but potentially lower long-term costs, whereas off-the-shelf products require less upfront but ongoing subscription fees.
- Risk tolerance: Building software carries development risks like limited scope and delays, while buying a software shifts technical risks to vendors but introduces dependency concerns.
For organizations considering AI integration, the decision can be complex. Custom solutions offer complete control over implementation. Whereas, purchased software may provide ready-made AI features, but with less flexibility for customization.
Indeed, before deciding whether to engage a custom software development company or purchase existing solutions, businesses must thoroughly assess their core competencies. They should determine which technological functions genuinely drive competitive advantage.
Buy vs. Build Analysis: When to Choose What?
Making the right build vs buy software decision requires a structured analytical approach. Rather than relying on gut feeling, successful organizations apply frameworks that align technology choices with business objectives.
One effective approach is the GSO framework that helps identify your primary objective:
- Growth: Attracting more customers or boosting revenue
- Scale: Expanding services sustainably by five to ten times
- Optimize: Enhancing profit margins or improving customer experience
After clarifying your objective, evaluate these key dimensions:
- Cost to build (immediate and long-term)45
- Cost to maintain (including baseline operational needs)
- Cost to buy (one-time and recurring subscription costs)
- Core expertise requirements
- Assess how crucial the software is for your business and if its ready for the market .
Buying makes the most sense when:
- The software isn't a core differentiator for your business
- Off-the-shelf products meet your key requirements
- You need a solution quickly (pre-built solutions accelerate time-to-market)
- Budget constraints limit upfront investment
- Your risk tolerance for development challenges is low
Building custom software becomes the optimal choice when:
- You have unique requirements that generic tools can't effectively support
- The software represents a strategic competitive advantage
- Your business model requires high innovation or customization
- You're planning for long-term scalability
- Market offerings lack maturity in your specific domain
Additionally, consider the total cost of ownership (TCO) beyond initial expenses. Although custom development typically involves higher upfront costs, it may deliver better long-term returns through improved efficiency and scalability.
For many organizations, a hybrid approach offers the best solution - purchasing a customizable platform that allows for API integration while maintaining core functionality.
Ultimately, the decision should align with your specific business context, available resources, and long-term strategic goals.
How do you know which option fits your Business Best?
Determining which path fits your business requires a systematic assessment of your specific situation. First thing to remember, successful build vs. buy software decisions start with evaluating your core competencies and strategic objectives.
Ask yourself these critical questions:
- Is this a core competency? If the software directly enhances your competitive advantage, building might make strategic sense. For instance, Amazon developed its warehousing infrastructure to maintain its logistics edge.
- How unique are your requirements? The more specialized your needs, the stronger the case for custom development. Hospitals have successfully implemented tailored patient-care systems that enhance operational efficiency.
- How quickly do you need the solution? Speed often favors buying. Pre-built cloud solutions like Salesforce offer ready-to-use features and comprehensive training for rapid deployment.
- What's your budget? Custom solutions typically involve higher upfront costs. Yet, companies like Uber demonstrate how strategic custom development yields long-term scalability.
- What's your risk tolerance? Building software carries risks like scope limitations and delays, while off-the-shelf solutions minimize these through proven tools.
Above all, evaluate your internal resources in a practical way. This includes assessing your financial position, human capital, operational capabilities, and strategic assets. For organizations with strong technical talent, building custom software often makes sense as a long-term investment.
Considering technical debt implications is equally important. Technical debt works like a hidden force gradually diminishing software value, with most companies running at 10% or higher Technical Debt Ratio (TDR).
Your decision ultimately shapes team satisfaction too, as 92% of employees report that having the right technology affects their job satisfaction.
Pros and Cons of Build and Buy Software
Weighing the strengths and limitations of each approach reveals significant trade-offs in the build vs buy software decision.
Pros of Building Software
- Full customization to meet unique business requirements
- Greater control over features, security, and data management
- Flexibility to scale or add new functions as the business grows
- Creates a unique competitive advantage with a tailor-made solution
Cons of Building Software
- High upfront costs for development and infrastructure
- Requires skilled developers and technical expertise
- Longer development time before deployment
- Ongoing maintenance and updates become the company’s responsibility
Pros of Buying Software
- Quick implementation with minimal setup time
- Lower initial investment compared to custom development
- Comes with vendor support, regular updates, and patches
- Proven reliability with pre-tested solutions and scalability options
Cons of Buying Software
- Limited customization for unique workflows
- Potential vendor lock-in and dependency
- May include unnecessary features that add complexity
- Risk of compatibility issues with existing systems
The build vs. buy decision is crucial for organizations exploring AI or API integration. Building software offers full customization and control but requires higher costs, expertise, and ongoing maintenance. Buying software enables faster deployment with vendor support and pre-built integrations, but may limit flexibility and create dependency. Understanding these trade-offs helps businesses choose the right path when working with a software development team or a custom software development company.
Buy vs Build Decision Framework: Steps Explained
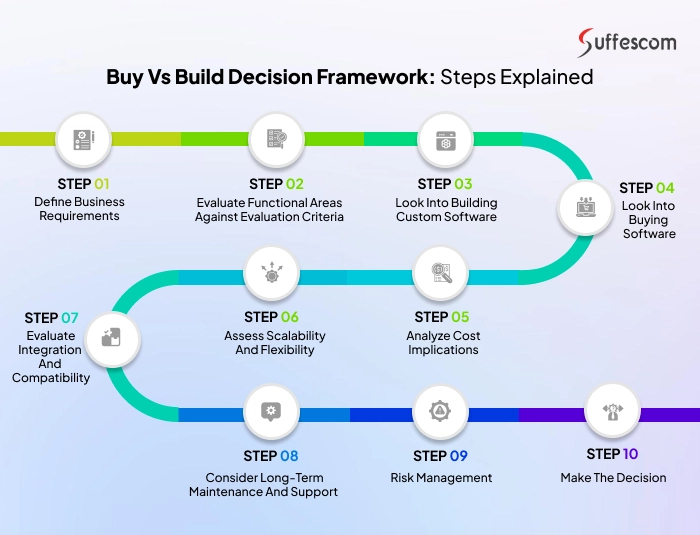
Choosing between building custom software and buying an off-the-shelf solution is rarely straightforward. Each option comes with its own benefits, challenges, and long-term implications. To make the right choice, businesses need a structured approach. The following step-by-step decision framework outlines key considerations—from defining requirements to managing risks. It can help organizations evaluate both options effectively and select the solution that best aligns with their goals.
Step 1: Define Business Requirements
Begin by clarifying your business goals, challenges, and must-have features. A well-defined set of requirements helps create a clear vision of what the software should achieve. This makes it easier to compare build vs buy options and avoid unnecessary features that don’t add value.
Step 2: Evaluate Functional Areas Against Evaluation Criteria
Examine how different departments and workflows will use the software. Create evaluation criteria such as performance, usability, compliance, and reporting. Mapping business needs to these criteria ensures the solution supports operations effectively and highlights any gaps that might require customization or additional investment.
Step 3: Look into Building Custom Software
Consider the potential benefits of building custom software. Evaluate whether your team has the expertise, resources, and time to create a tailored solution. Custom software offers complete flexibility, but it often demands significant investment and ongoing maintenance that should be carefully assessed before moving forward.
Step 4: Look into Buying Software
Explore the commercial off-the-shelf solutions available in the market. Compare vendors based on functionality, reliability, security, and scalability. Buying software often ensures faster deployment and lower upfront costs. But it may include unnecessary features or limit customization, which could affect long-term alignment with unique business processes.
Step 5: Analyze Cost Implications
Assess the total cost of ownership for both options, including development, licensing, infrastructure, and support. While building requires larger upfront investments, buying may incur recurring subscription fees. Carefully analyzing costs helps determine which approach offers the best long-term return on investment for your organization.
Step 6: Assess Scalability and Flexibility
Evaluate whether the solution can adapt as your business grows or evolves. Custom-built software offers greater flexibility to scale, while purchased solutions may provide limited scalability depending on vendor offerings. Prioritizing scalability ensures the chosen option won’t restrict future expansion or technological adoption.
Step 7: Evaluate Integration and Compatibility
Ensure that the software integrates seamlessly with your existing systems, APIs, and workflows. Compatibility issues can cause delays, increase costs, and reduce efficiency. Both custom and pre-built solutions must be analyzed for how well they fit into your current technology ecosystem without causing disruptions.
Step 8: Consider Long-Term Maintenance and Support
Look beyond the initial setup to understand ongoing support and maintenance needs. Building software requires an in-house team for updates and bug fixes, while buying often comes with vendor-provided support. This step ensures the software remains secure, updated, and reliable in the long term.
Step 9: Risk Management
Identify potential risks associated with both options, such as vendor lock-in, project delays, hidden costs, or cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Create a plan to mitigate these risks through contracts, backup strategies, or additional safeguards. Effective risk management protects your business from disruptions and unforeseen expenses.
Step 10: Make the Decision
After thoroughly evaluating all factors, make a well-informed decision that aligns with your business goals, budget, and growth strategy. Consider the cost, customization, scalability, and long-term sustainability to make the right choice. Ensure the software investment delivers maximum value to the organization over time.
How does the Build vs Buy Software Analysis Decision Differ for Startups vs Enterprises?
Startups and enterprises navigate the build vs buy software spectrum from opposite ends, primarily due to their distinct priorities and resources.
Startups typically prioritize speed and resource efficiency when making technology decisions. With limited funding and small teams, startups need solutions that deliver immediate value without draining precious resources. Consequently, many young businesses are choosing ready-to-use platforms like Shopify that provide comprehensive functionality without requiring custom code. This approach allows startups to focus on testing their ideas, acquiring customers, and achieving rapid growth instead of investing heavily in infrastructure development.
In contrast, enterprises operate within complex environments where standard solutions often fail to meet specialized needs. Given their larger scale, enterprises running hundreds of applications—anywhere from 300 to 600 on average—face integration challenges that startups rarely encounter. For large organizations with 10,000+ employees, SaaS spending can reach as much as $224.80 million annually, making build decisions more financially justifiable for core functions.
Netflix exemplifies this enterprise approach. When commercial CDNs couldn't support their massive scale requirements, they built their own content delivery network (Open Connect) to optimize streaming quality. This strategic decision delivered long-term control over a business-critical system.
Considering these differences, the build vs buy framework must be applied with organizational context in mind. While startups buy to stay lean, enterprises build to gain competitive advantages in their core functions.
Build vs Buy Software Analysis: Get Expert Insights
Unsure whether to invest in custom development or off-the-shelf solutions? Speak with our experts and get actionable insights tailored to your industry.
2025 Tech Landscape's Impact on Buy vs Build Software
As we approach 2025, technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping the build vs buy software equation. The enterprise software market alone is projected to reach nearly $295 billion by the end of 2024, creating both opportunities and complexities for decision-makers.
Low-code/no-code platforms are blurring traditional boundaries between building and buying software. These tools enable non-technical users to create applications quickly without extensive expertise. This makes custom development more accessible while maintaining the efficiency typically associated with commercial solutions.
API-first commercial solutions offer greater flexibility. Modern vendors provide comprehensive APIs for customization and integration. It allows businesses to combine different tools into tailored systems while maintaining the reliability of commercial software.
AI integration has become a decisive factor in this landscape. With 66% of companies investing in AI before the end of 2024 expecting positive impacts, organizations must assess whether commercial AI solutions meet their needs or if custom AI models would deliver genuine advantages.
Cloud-native architecture is correspondingly simplifying custom software management by reducing infrastructure complexity. Modern cloud platforms enable managing of services that streamline tasks once requiring specialized expertise.
Throughout this evolution, data ownership considerations have grown increasingly crucial. The ability to maintain control over business data while leveraging advanced analytics capabilities now profoundly influences whether organizations build proprietary solutions or rely on vendor alternatives.
Cost Comparison: Build vs Buy Software
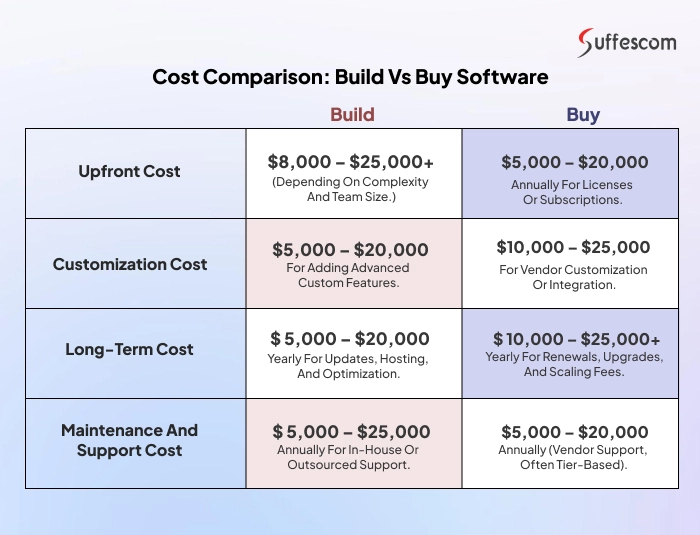
Upfront Cost
- Build: $8,000 – $25,000+ depending on complexity and team size.
- Buy: $5,000 – $20,000 annually for licenses or subscriptions.
Customization Cost
- Build: $5,000 – $20,000 for adding advanced custom features.
- Buy: $10,000 – $25,000 for vendor customization or integration.
Long-Term Cost
- Build: $ 5,000 – $20,000 yearly for updates, hosting, and optimization.
- Buy: $ 10,000 – $25,000+ yearly for renewals, upgrades, and scaling fees.
Maintenance and Support Cost
- Build: $ 5,000 – $25,000 annually for in-house or outsourced support.
- Buy: $5,000 – $20,000 annually (vendor support, often tier-based).
Why Choose Suffescom to Build Software?
When deciding to build custom software, selecting the right development partner becomes pivotal to your success. Suffescom stands out with 13+ years of industry expertise and a global team of 750+ technical professionals.
Primarily, what distinguishes Suffescom is its unwavering commitment to on-time delivery alongside transparent communication throughout the development process. Their seasoned developers excel in implementing innovative technologies and modern tools to create solutions that directly address business challenges.
Throughout their journey, Suffescom has built a reputation for customer satisfaction, evidently shown in client testimonials praising their ability to develop custom modules by effectively understanding business needs. This client-centered approach extends to their 24/7 technical support team that addresses queries and provides immediate solutions.
Despite the complexity of custom development, Suffescom offers free consultation services where businesses can discuss project requirements and receive cost estimates from technical experts. Their affordable pricing strategy ensures robust, secure, and bug-free software development without compromising quality.
From AI integration capabilities to API-first development approaches, their team delivers scalable architectures that evolve with your business. Our track record of successful MVPs and complex enterprise solutions positions us as a reliable partner for businesses choosing the "build" path in the build vs buy software decision.
Conclusion
The build vs buy software decision remains one of the most significant strategic choices businesses face today. Throughout this analysis, we've seen how multiple factors influence this decision, from cost considerations and unique business requirements to time constraints and risk tolerance. Companies must evaluate whether software represents a core competency that drives competitive advantage before committing to either path.
Startups generally benefit from buying ready-made solutions that conserve precious resources while enabling rapid market entry. Enterprises, however, often justify custom development for specialized needs that off-the-shelf products simply cannot address. Netflix and Amazon exemplify this approach through their strategic investments in proprietary technology that directly supports their business models.
The decision framework we've outlined provides a systematic approach to this complex choice. First, clarify your primary business objectives using the GSO framework. Then, thoroughly assess your requirements, available resources, and long-term strategic goals. This structured evaluation helps prevent costly mistakes and aligns technology decisions with business strategy.
Technology trends continue to reshape this landscape as we move toward 2025. Low-code platforms blur traditional boundaries while API-first solutions offer unprecedented flexibility. AI integration capabilities have become crucial considerations, affecting whether commercial solutions meet needs or custom development delivers genuine advantages.
Many businesses find success through hybrid approaches that combine purchased platforms with custom elements. This strategy balances immediate implementation benefits with tailored capabilities that address specific business challenges.
After all, the best choice depends entirely on your unique situation. Whether you build custom software with development partners like Suffescom or purchase existing solutions with AI integration capabilities, success comes from aligning technology decisions with your organization's core competencies and strategic objectives. Though this decision requires careful consideration, the systematic framework provided here equips you with the tools needed to make an informed choice that drives your business forward.
FAQs
What key factors should I consider when evaluating off-the-shelf software?
Look beyond initial price tags to examine support levels (email, chat, telephone), company stability, integration capabilities, and security measures. Consider the user experience and necessity of training while making a decision.
How long does custom software development typically take?
Custom development time frames vary based on complexity—MVPs typically require 6-10 weeks, whereas advanced platforms may take 4-6 months. Factors like integrations and compliance requirements can increase the duration.
Do I own the source code if I choose custom development?
Yes, you will receive full ownership of the source code after project completion and final payment. This provides complete control over your software.
Is building software in-house always risky?
Data shows building software in-house carries significant risks—54% of projects exceed original budgets by nearly 200%, and organizations cancel 31% of projects. Furthermore, the failure rate for building software is two in every three projects.
When might a hybrid build-buy approach make sense?
A hybrid approach is effective when you need immediate core functionality but also require specialized features. This can help you to get the benefit of ready-made components while developing custom elements for your unique requirements.